Dr. Ganivada Hyma has published this extensive guide on PCOS encompassing its causes, symptoms, treatments, and management.
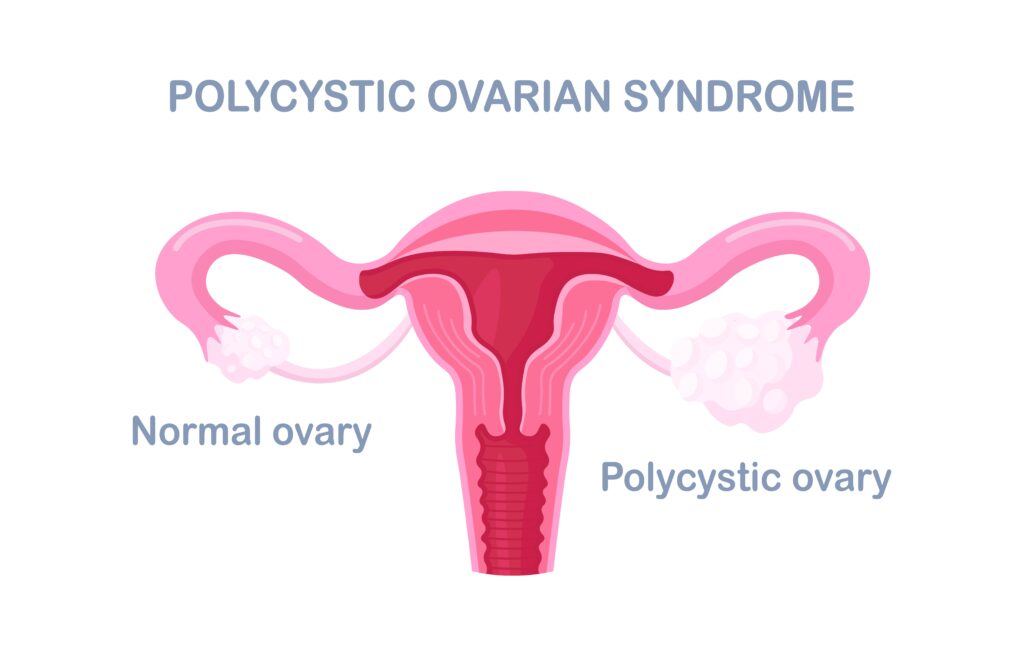
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age(4-18%). It is characterized by an imbalance of hormones, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and other symptoms such as infertility, acne, excessive hair growth, and weight gain. PCOS can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life and increase the risk for certain health conditions if left untreated. It’s not only a gynecological problem but encompasses metabolic, dermatological, and psychological disorders.PCOS is characterized by hyperandrogenism, anovulation or oligo ovulation, and polycystic ovaries.
PCOS is a common cause of infertility in women with anovulatory cycles ( up to 90%)
In India, PCOS increased by 30%.
What are the 4 causes of PCOS
Several factors that may contribute to PCOS are:
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS may have insulin resistance, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Imbalance: An imbalance in reproductive hormones can lead to issues with ovulation. Elevated levels of androgens interfere with the development of ovarian follicles and the release of eggs.
- Genetics: PCOS often runs in families, indicating a genetic connection.
- Inflammation: Low-grade inflammation is common in women with PCOS, contributing to insulin resistance.
How to diagnose PCOS?
The criteria for diagnosis may include at least two of the following:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles.
- Elevated androgen levels.
- Polycystic ovaries are visible on an ultrasound.
What are the symptoms of PCOS
It is characterized by an imbalance of hormones, which can lead to various symptoms. Common signs and symptoms associated with PCOS include hirsutism, irregular menstrual cycles( amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea), infertility, polycystic ovaries, acne, androgenic alopecia, obesity, acne, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, and virilization.
Increases early pregnancy loss, Gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, and preterm labor during pregnancy.
- Polycystic Ovaries: 50-75% of women with PCOS symptoms have polycystic ovaries on ultrasound.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycle: women can have fewer cycles( have a long gap between menses) or absent menstrual cycles for several months. women can even present with heavy menstrual cycles and DUB.
- Infertility: up to 55-75% of women cannot get pregnant due to PCOS (female infertility factor).
- Hirsutism: excessive terminal hair growth over androgen-dependent areas like the upper lip, chin, abdomen, legs, etc
- Excess Androgen Levels: Elevated levels of male hormones (androgens) may lead to signs such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism) and severe acne.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS may experience weight gain or find it challenging to lose weight.
- Skin Issues: Darkening of the skin, especially along neck creases, in the groin, and underneath breasts, and skin tags can be more common.
- Hair Thinning: Hair loss from the scalp may occur in some women.
12 Long-term effects of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is more than just a reproductive health issue, it has far-reaching effects on a woman’s overall health. Understanding these long-term effects is crucial for managing the condition and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This blog explores the various long-term health implications associated with PCOS.
- Infertility: One of the most significant long-term effects of PCOS is infertility. Due to irregular ovulation or anovulation (lack of ovulation), women with PCOS may often face challenges in conceiving. While fertility treatments can help, the journey to parenthood can be longer and more complex for those with PCOS.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin resistance is a common feature of PCOS, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Studies show that women with PCOS are four times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes compared to those without the condition. This risk is particularly heightened in women who are overweight or obese.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Women with PCOS may have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and heart disease. The hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and inflammation associated with PCOS contribute to these increased risks. Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health is essential for women with PCOS.
- Endometrial Cancer: PCOS may lead to prolonged periods of unopposed estrogen (without the counteracting effect of progesterone), which can cause the endometrium (lining of the uterus) to thicken excessively. This condition, known as endometrial hyperplasia, can increase the risk of endometrial cancer. Regular menstrual cycles or the use of progestin can help reduce this risk.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea, a condition characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. This is often linked to obesity, a common issue in women with PCOS. Sleep apnea can lead to further health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
- Mental Health Issues: PCOS can take a toll on mental health, leading to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and eating disorders. The physical symptoms of PCOS, such as weight gain, acne, and excess hair growth, may also impact self esteem and body image, exacerbating mental health challenges. Psychological support and counseling can be vital components of PCOS management.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Metabolic syndrome is a group of conditions that raise the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Women with PCOS are more likely to develop metabolic syndrome, which includes symptoms such as abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is more prevalent in women with PCOS due to insulin resistance and obesity. NAFLD can progress to more severe liver damage, including non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and liver failure.
- Pregnancy Complications: Women with PCOS who do become pregnant may face a higher risk of complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm birth. Careful monitoring and management during pregnancy are essential to reduce these risks.
- Dyslipidemia: Dyslipidemia, characterized by abnormal levels of lipids in the blood, is more common in women with PCOS. This condition includes elevated levels of total cholesterol, LDL (bad cholesterol), and triglycerides, and reduced levels of HDL (good cholesterol). Dyslipidemia significantly increases the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
- HyperAndrogenism: Hyperandrogenism, or elevated levels of male hormones (androgens), is a hallmark of PCOS. This may lead to physical symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness. Hyperandrogenism can also exacerbate insulin resistance and contribute to metabolic disturbances.
- Carcinoma: In addition to endometrial cancer, women with PCOS may have an elevated risk of other cancers. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular screenings is advised.
5 Treatment Options for PCOS
Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments available for PCOS that can help manage symptoms and improve fertility. This article will explore some of the natural treatment options for PCOS available today.
- Exercise: One of the best treatment options to incorporate into your daily life when suffering from PCOS is Yoga and Meditation. It not only helps you physically challenge this battle but also supports your mental strength. Yoga & Meditation experts are available to understand and design a framework that suits your lifestyle. 30-60 minutes a day is recommended. Exercise increases insulin sensitivity.
- Lifestyle Modification: Many women with PCOS gain weight. Weight reduction can help to reduce obesity(5-10% weight loss) and improve menstrual irregularity in 90% of cases, which can lead to a reduced risk of health complications. spontaneous pregnancy occurs in some women up to 30%. Weight loss should be based on a healthy diet and increased physical activity.
- Diet: high fiber, complex carbohydrates, and low saturated fats are recommended. Avoidance of fast foods and saturated fats in routine is needed.
- Treatment: Many hormone treatments are available for PCOS, which contain progesterone or estrogen and progesterone combination. These therapies might help by improving your regular periods or reducing the symptoms of PCOS. Metformin is an insulin sensitizer that helps to improve ovulation in up to 50% of cases.
Monitoring of PCOS
Visiting a healthcare provider yearly is vital for women with PCOS. These check-ups should include:
- Hormonal Assessments: Regular blood tests to check levels of androgens, insulin, and other hormones can help in adjusting treatment plans and managing symptoms.
- Glucose Tolerance Tests: Monitoring blood sugar levels and insulin resistance is crucial to prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- Lipid Profile: Regular lipid profiles can help track cholesterol and triglyceride levels, essential for preventing cardiovascular disease.
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Elevated blood pressure is a common concern in PCOS, so regular monitoring is necessary to detect and manage hypertension.
- Pelvic Ultrasounds: Periodic ultrasounds can monitor ovarian cysts and endometrial thickness, helping in the early detection of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
- Weight and BMI Checks: Tracking weight and body mass index (BMI) helps in managing obesity-related risks.
Impact of PCOS on Pregnancy & Fertility
An Obstetrics & Gynaecology Specialist and/or an Infertility Specialist Doctor will discuss the impact of PCOS on pregnancy and fertility, as well as the available treatments to help improve fertility outcomes in women with PCOS.
I am Dr. Ganivada Hyma, available for online video consultation here: click here
You can call our team to book appointments with me at 90534 90543 or visit the website.
Other Health Articles:
Irregular Periods: 10 Powerful Strategies to Reclaim Hormonal Harmony
PCOD Diet Chart for Weight Loss: The Key to a Slimmer You
Can a UTI Affect Your Period? Exploring the Surprising Connections and the Role of Lab Tests
Best Diet Plan for PCOD: Expert Tips by Dietitian Neha Suryawanshi | Medicas Video Podcast
5 Safe and Effective Ways to Start Your Period Naturally: Methods and Risks Explained
Disclaimer
Medical Advice: The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding your specific medical condition.
Accuracy of Information: While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, the field of medicine and viral fevers is constantly evolving. The content in this blog post may not reflect the most current research or medical guidelines. Therefore, it is advisable to cross-check any information provided with reliable sources or consult a healthcare professional.
Individual Variations: The symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures discussed in this blog post are general in nature and may not apply to everyone. It is important to remember that each individual’s situation is unique, and personalized medical advice should be sought when making healthcare decisions.
External Links: This blog post may contain links to external websites or resources for additional information. However, we do not endorse or have control over the content of these third-party websites. Accessing these links is done at your own risk, and we are not responsible for any consequences or damages that may arise from visiting these external sources.
Results May Vary: The effectiveness of treatment options or preventive measures mentioned in this blog post may vary from person to person. What works for one individual may not work the same way for another. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.

Dr. Ganivada Hyma is an experienced doctor with 7+ years in Obstetrics & Gynaecology. An MBBS graudate from Guntur Medical College, Guntur in 2012. Holds Post Graduate degree, Diploma in Obstetrics & Gynaecology (DGO) from Andhra Medical College (KGH), Visakhapatnam in 2018. DNB from Narayana Hrudayalaya Hospital, Bangalore.


