Introduction
Diabetes is a complex metabolic condition that affects millions of individuals around the globe. While most people are familiar with the common complications of diabetes, such as neuropathy and retinopathy, there’s a lesser-known yet equally important aspect to consider: the impact of diabetes on oral health.
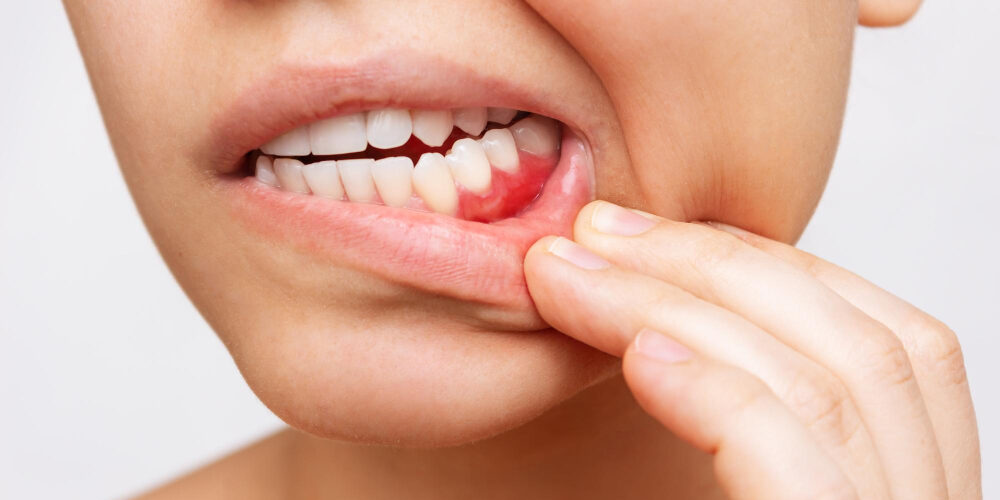
Diabetic ulcers and sores that develop in the mouth can pose significant challenges, often requiring specialized care to prevent further complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, risks, and detailed strategies for effectively managing and caring for diabetic ulcers and sores in the mouth, ensuring optimal oral health for individuals living with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetic Ulcers and Sores in the Mouth
Diabetic ulcers and sores in the mouth, also known as oral ulcers or diabetic stomatitis, are a manifestation of the systemic effects of diabetes. Elevated blood sugar levels can compromise the body’s ability to fight infections and impede the healing process. As a result, the delicate oral tissues may develop red or white patches, painful lesions, or open sores that can be particularly uncomfortable and distressing for those affected. Moreover, untreated ulcers and sores can become breeding grounds for bacteria, potentially leading to infections that could further exacerbate the situation.
Caring for Diabetic Ulcers and Sores
- Holistic Blood Sugar Management: Central to effective management is maintaining optimal blood sugar control. Collaborate closely with your healthcare provider to establish a comprehensive diabetes management plan that includes regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to prescribed medications, and a balanced diet. Consistently stable blood sugar levels can facilitate the healing process and reduce the risk of developing new ulcers and sores.
- Elevated Oral Hygiene Practice: Vigilant oral hygiene is paramount when dealing with diabetic ulcers and sores. Employ a soft-bristle toothbrush to gently clean your teeth at least twice a day. Use fluoride toothpaste to fortify tooth enamel and meticulously clean all surfaces of your teeth. Devote attention to cleaning your tongue, as it can harbor harmful bacteria that contribute to ulcer formation.
- Selective Oral Care Products: Be selective in your choice of oral care products. Opt for alcohol-free mouthwashes and moisturizing toothpaste to prevent further irritation to your mouth’s delicate tissues. Refrain from using abrasive toothbrushes and toothpaste, as these can aggravate existing ulcers.
- Sufficient Hydration: Proper hydration is indispensable for maintaining oral health. Adequate water intake ensures sufficient saliva production, which contains enzymes that aid in digestion and offer protective benefits against harmful bacteria. Dry mouth can exacerbate the development of ulcers, so sip water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist.
- Mindful Dietary Choices: When managing diabetic ulcers and sores, making mindful dietary choices is essential. Opt for nutrient-rich, soft-textured foods that are easy to chew and won’t irritate your mouth. Consider incorporating yogurt, mashed vegetables, smoothies, and lean proteins into your diet. Conversely, avoid foods that are spicy, acidic, or excessively crunchy, as they can worsen existing sores.
- Tobacco Cessation: Smoking and tobacco use can severely compromise blood circulation and impede the body’s natural healing processes. Kicking the habit not only promotes better oral health but also significantly reduces the risk of developing new ulcers and sores.
- Saline Solution Rinses: Saline solution rinses can offer soothing relief and promote oral cleanliness. Prepare a saline mixture by dissolving approximately half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water. Gently swish this solution in your mouth after meals or as needed to aid in healing and mitigate the risk of infection.
- Regular Professional Dental Care: Scheduled dental check-ups are paramount for individuals with diabetes. Consistent visits to your dentist facilitate the early detection of oral health issues and allow for professional guidance on managing diabetic ulcers and sores. Your dentist may recommend tailored treatments or medications to expedite the healing process and enhance oral health.
Conclusion
Effective care for diabetic ulcers and sores in the mouth necessitates a comprehensive approach that revolves around meticulous blood sugar control, vigilant oral hygiene, and judicious dietary selections. By implementing the proactive measures and adhering to the guidelines detailed in this guide, you can alleviate the discomfort associated with these ulcers and sores, mitigate the likelihood of complications, and uphold optimal oral health. Remember to always collaborate closely with your healthcare provider and dentist to receive personalized advice and treatment options that align with your individual needs and circumstances.
Other Health Articles
Understanding Type 4 Diabetes: Symptoms and Effective Prevention Strategies
Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Types, and Risk Factors
The Role of Nutrition in Diabetes Management
Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Dry Eyes
Normal Blood Sugar Levels Chart By Age: Understanding Optimal Health
A Comprehensive Guide on How to Test Blood Sugar at Home
Effective Strategies for Managing Swollen Feet Due to Diabetes
Disclaimer:
Medical Advice: The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance regarding your specific medical condition.
Accuracy of Information: While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, the field of medicine and viral fevers is constantly evolving. The content in this blog post may not reflect the most current research or medical guidelines. Therefore, it is advisable to cross-check any information provided with reliable sources or consult a healthcare professional.
Individual Variations: The symptoms, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures discussed in this blog post are general in nature and may not apply to everyone. It is important to remember that each individual’s situation is unique, and personalized medical advice should be sought when making healthcare decisions.
External Links: This blog post may contain links to external websites or resources for additional information. However, we do not endorse or have control over the content of these third-party websites. Accessing these links is done at your own risk, and we are not responsible for any consequences or damages that may arise from visiting these external sources.
Results May Vary: The effectiveness of treatment options or preventive measures mentioned in this blog post may vary from person to person. What works for one

Chief Consultant Diabetologist & Preventive Cardiologist, Consultant Functional and Lifestyle Medicine, Geriatrician & Family Medicine Specialist, Nutritionist, Life Counsellor and Wellness Coach, Motivational Speaker & Columnist, NLP Practitioner and Hypnotherapist, Bach flower Therapist